黃斑變性:AMD的診斷和危險因素預測模型
年齡相關性黃斑變性(AMD) 嚴重影響中心視力,目前在臨床上沒有十分有效的治療方法,是發達國家老年人喪失視力的重要疾病。AMD的發病和進展與多個基因和環境的風險因素相關,包括吸煙、體重指數(BMI)等。預測AMD疾病進展的模型或可幫助醫生治療AMD患者。國家“千人計劃”入選者、華西醫院眼科教授張康教授與其在美國的同事一起,收集了自晚期 AMD患者,中期AMD患者及健康對照組的三組數據,并建立了預測模型。研究者結合15個與AMD發生發展相關的基因變異以及個體的吸煙情況與BMI指數,最終建立了一個AMD發展預測模型,建立的預測模型可以給臨床上的診斷、治療和預后判斷提供依據,為AMD患者的個體化治療帶來希望。
Macular degeneration: Predictive model combines genetic and environmental factors
A new model for assessing disease progression of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) may improve the therapeutic responses of patients. The onset and progression of AMD — a leading cause of vision loss in seniors in developed countries — are linked to multiple genetic and environmental risk factors, including smoking and body mass index (BMI). Kang Zhang of University of California, San Diego with colleagues in the USA and China, has developed a prediction model by collecting data from three groups: patients with advanced AMD, those with intermediate AMD and a normal group. The researchers combined data for genetic variations within 15 genes previously linked to AMD risk with smoking status and BMI of individuals in the three groups. This resulted in a highly predictive model for AMD progression that is promising for improving personalized therapy of patients.
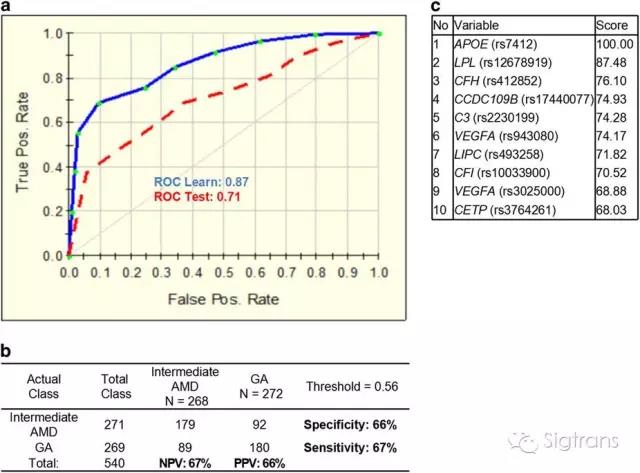
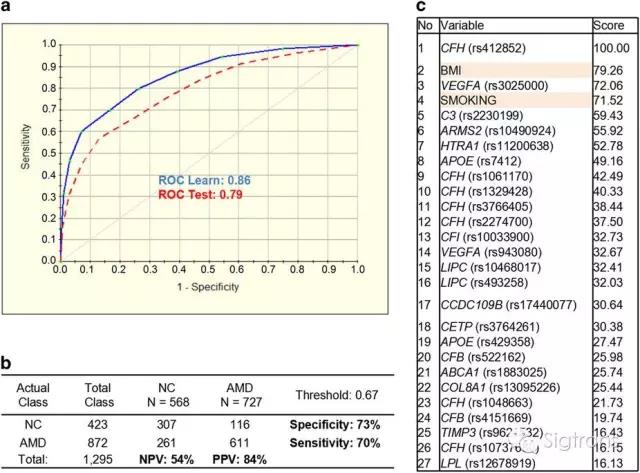
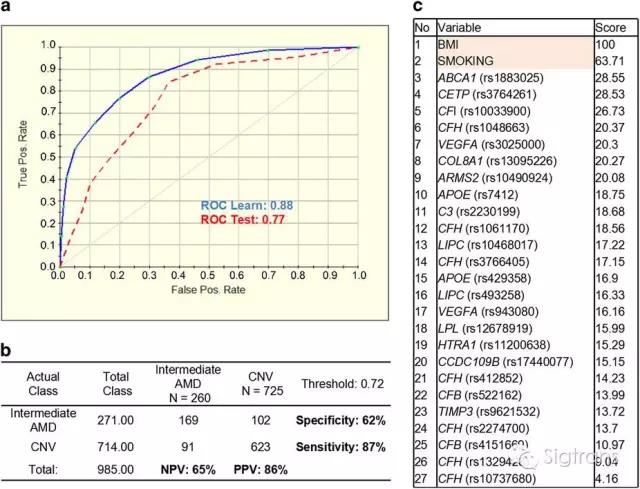
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is characterized by complex interactions between genetic and environmental factors. Here we genotyped the selected 25 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in 983 cases with advanced AMD and 271 cases with intermediate AMD and build an AMD life-risk score model for assessment of progression from intermediate to advanced AMD. We analyzed the performance of the prediction model for geographic atrophy progressors or choroidal neovascularization progressors versus non-progressors based on the 25 SNPs plus body mass index and smoking status. Our results suggest that a class prediction algorithm can be used for the risk assessment of progression from intermediate to late AMD stages. The algorithm could also be potentially applied for therapeutic response, and toward personalized care and precision medicine.
Wenqiu Wang, Katarzyna Gawlik, Joe Lopez, Cindy Wen, Jie Zhu, Frances Wu, William Shi, Samuel Scheibler, Huimin Cai, Ram Vairavan, Alexander Shi, Weldon Haw, Henry Ferreyra, Ming Zhang, Sherman Chang & Kang Zhang. Genetic and environmental factors strongly influence risk, severity and progression of age-related macular degeneration. Signal transduction and targeted therapy,1. (2016). doi:10.1038/sigtrans.2016.16