Sigtrans
癌癥:通過阻塞核輸出抑制腫瘤生長
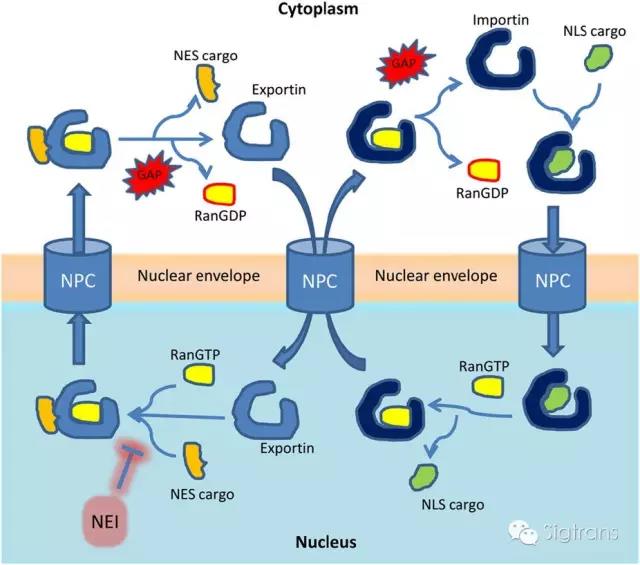
CRM1,參與從細胞核轉運出蛋白質和RNA的蛋白,是一個有吸引力的癌癥治療靶點。在這篇綜述中,來自四川大學的孫慶祥教授與賈大教授領導介紹了出核因子CRM1在癌癥發展中扮演的角色。CRM1能介導分子從細胞核進入胞漿,CRM1在肺癌、腦癌、肝癌及其他器官癌癥中高表達,并且其活性與病人的治療結果有關。部分CRM1抑制劑已經進入臨床試驗,但并不算成功。在本文中,作者比較和對比不同CRM1抑制劑的作用機制,并著重介紹了一種新型的非共價CRM1抑制劑,比起以往的抑制劑,這種新型抑制副作用小且更不容易耐藥。
Cancer: Blocking nuclear export to halt tumor growth
A protein involved in transporting proteins and RNAs out of the cell nucleus offers an attractive target for treating cancer. In a review article, a team led by Qingxiang Sun and Da Jia from Sichuan University, China, discuss the role of the nuclear export factor CRM1 in cancer development. CRM1—which mediates the exit of molecular cargo out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm—is overexpressed in tumors of the lungs, brain, liver and other organs, and its activity is associated with poor patient outcomes. Drugs that block CRM1 have been tested in clinical trials, with middling success. The authors outline a strategy for a new kind of CRM1 inhibitor that should produce fewer side effects and be less prone to drug resistance than existing agents.
Abstract
Treating cancer through inhibition of nuclear export is one of the best examples of basic research translation into clinical application. Nuclear export factor chromosomal region maintenance 1 (CRM1; Xpo1 and exportin-1) controls cellular localization and function of numerous proteins that are critical for the development of many cancer hallmarks. The diverse actions of CRM1 are likely to explain the broad ranging anti-cancer potency of CRM1 inhibitors observed in pre-clinical studies and/or clinical trials (phase I–III) on both advanced-stage solid and hematological tumors. In this review, we compare and contrast the mechanisms of action of different CRM1 inhibitors, and discuss the potential benefit of unexplored non-covalent CRM1 inhibitors. This emerging field has uncovered that nuclear export inhibition is well poised as an attractive target towards low-toxicity broad-spectrum potent anti-cancer therapy.
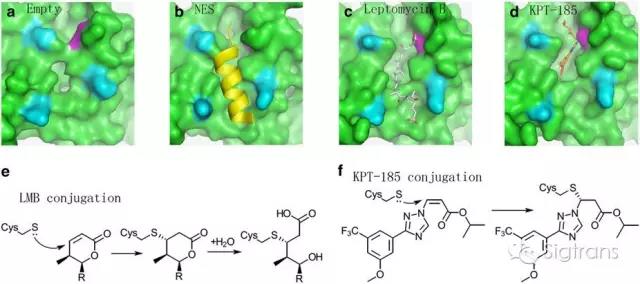
圖1 不同的CRM1抑制劑的作用機制
Qingxiang Sun, Xueqin Chen, Qiao Zhou, Ezra Burstein, Shengyong Yang, Da Jia. Inhibiting cancer cell hallmark features through nuclear export inhibition. Signal transduction and targeted therapy, 1. (2016). doi:10.1038/sigtrans.2016.10